Extra high superoxide dismutase in host tissue is associated with
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 16 junho 2024
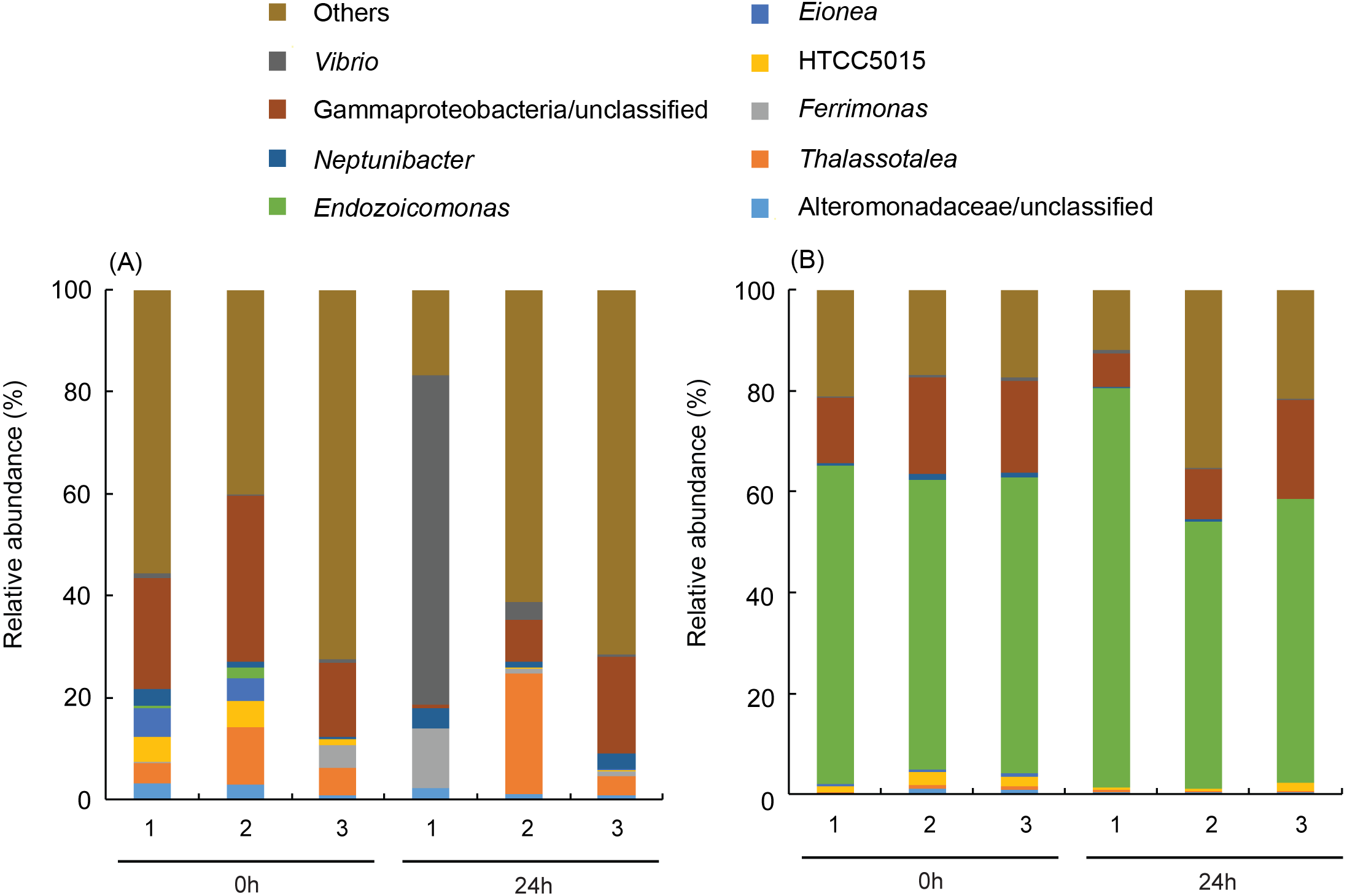
Global warming threatens reef-building corals with large-scale bleaching events; therefore, it is important to discover potential adaptive capabilities for increasing their temperature resistance before it is too late. This study presents two coral species (Platygyra verweyi and Isopora palifera) surviving on a reef having regular hot water influxes via a nearby nuclear power plant that exhibited completely different bleaching susceptibilities to thermal stress, even though both species shared several so-called “winner” characteristics (e.g., containing Durusdinium trenchii, thick tissue, etc.). During acute heating treatment, algal density did not decline in P. verweyi corals within three days of being directly transferred from 25 to 31 °C; however, the same treatment caused I. palifera to lose < 70% of its algal symbionts within 24 h. The most distinctive feature between the two coral species was an overwhelmingly higher constitutive superoxide dismutase (ca. 10-fold) and catalase (ca. 3-fold) in P. verweyi over I. palifera. Moreover, P. verweyi also contained significantly higher saturated and lower mono-unsaturated fatty acids, especially a long-chain saturated fatty acid (C22:0), than I. palifera, and was consistently associated with the symbiotic bacteria Endozoicomonas, which was not found in I. palifera. However, antibiotic treatment and inoculation tests did not support Endozoicomonas having a direct contribution to thermal resistance. This study highlights that, besides its association with a thermally tolerable algal symbiont, a high level of constitutive antioxidant enzymes in the coral host is crucial for coral survivorship in the more fluctuating and higher temperature environments.

Superoxide Dismutase: A Key Enzyme for the Survival of Intracellular Pathogens in Host

Catalase, a therapeutic target in the reversal of estrogen-mediated aging: Molecular Therapy
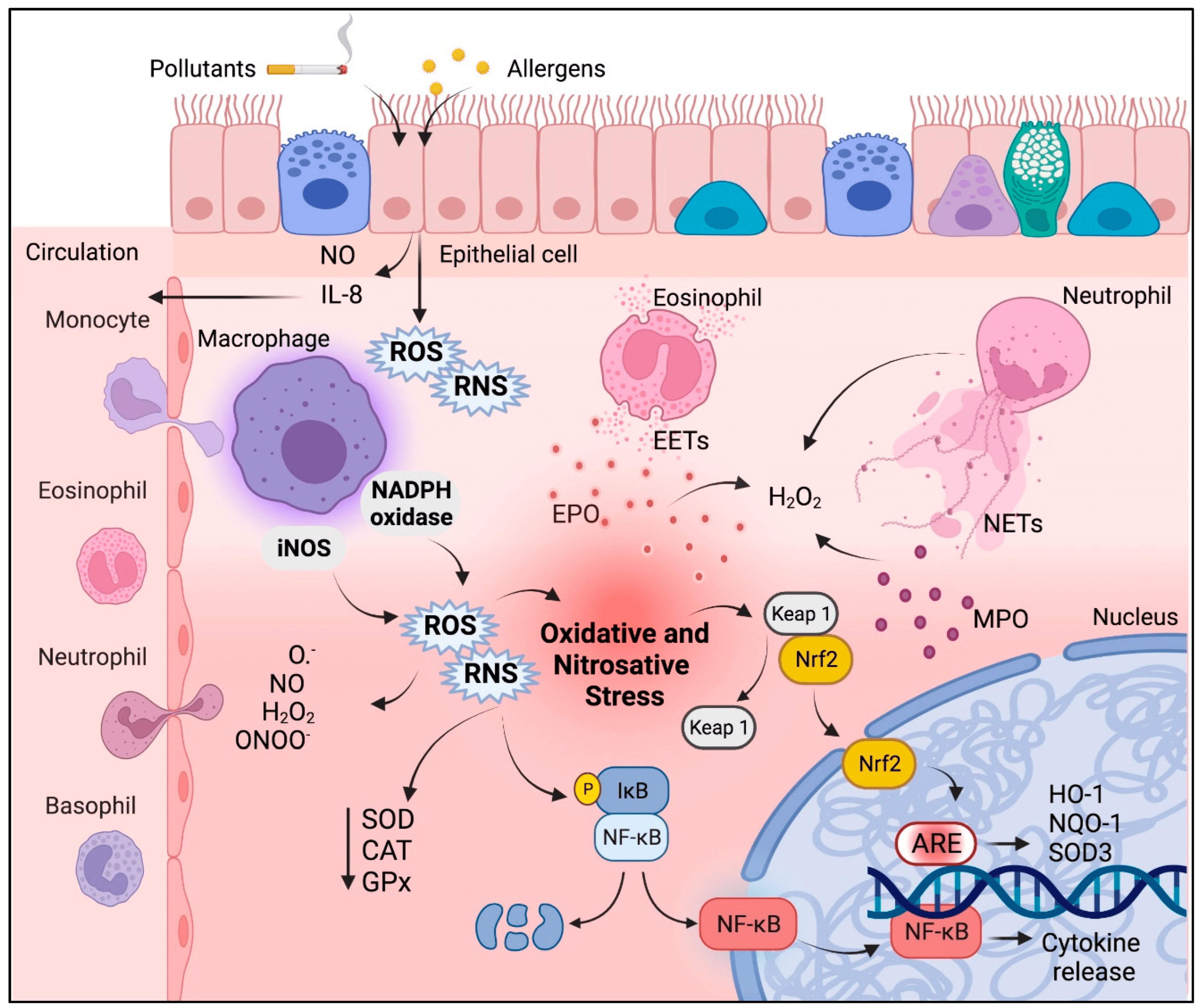
Antioxidants, Free Full-Text

Multi-omics analyses reveal bacteria and catalase associated with keloid disease - eBioMedicine

Expression of superoxide dismutase (SOD) in the kidney after gene
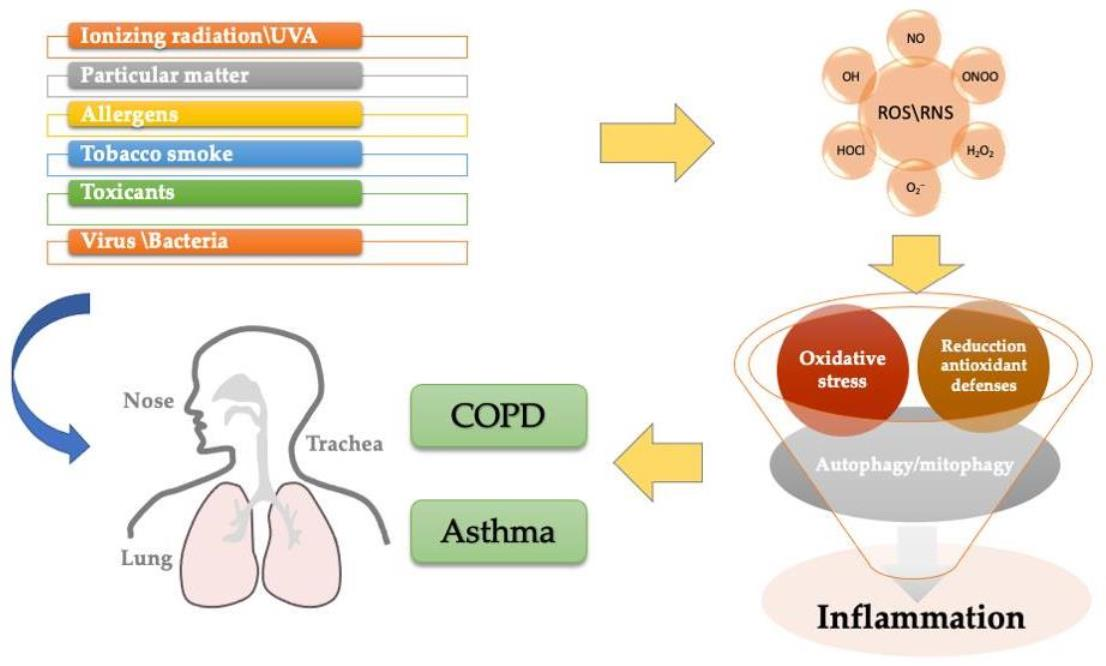
Antioxidants, Free Full-Text
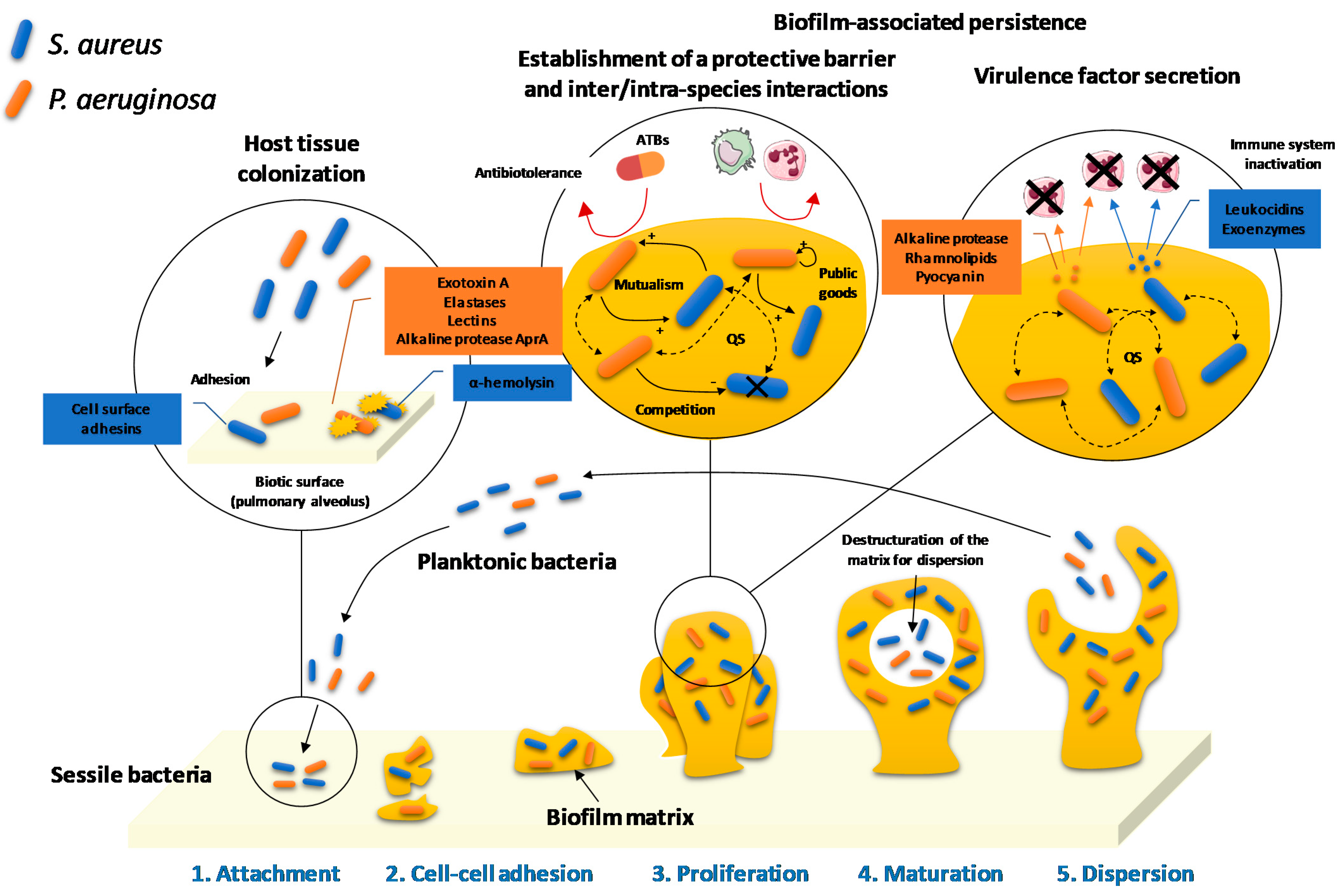
Pharmaceuticals, Free Full-Text

PDF) Superoxide Dismutase: A Biomarker for Early Diagnosis of Tuberculosis

Propionate induces intestinal oxidative stress via Sod2 propionylation in zebrafish - ScienceDirect
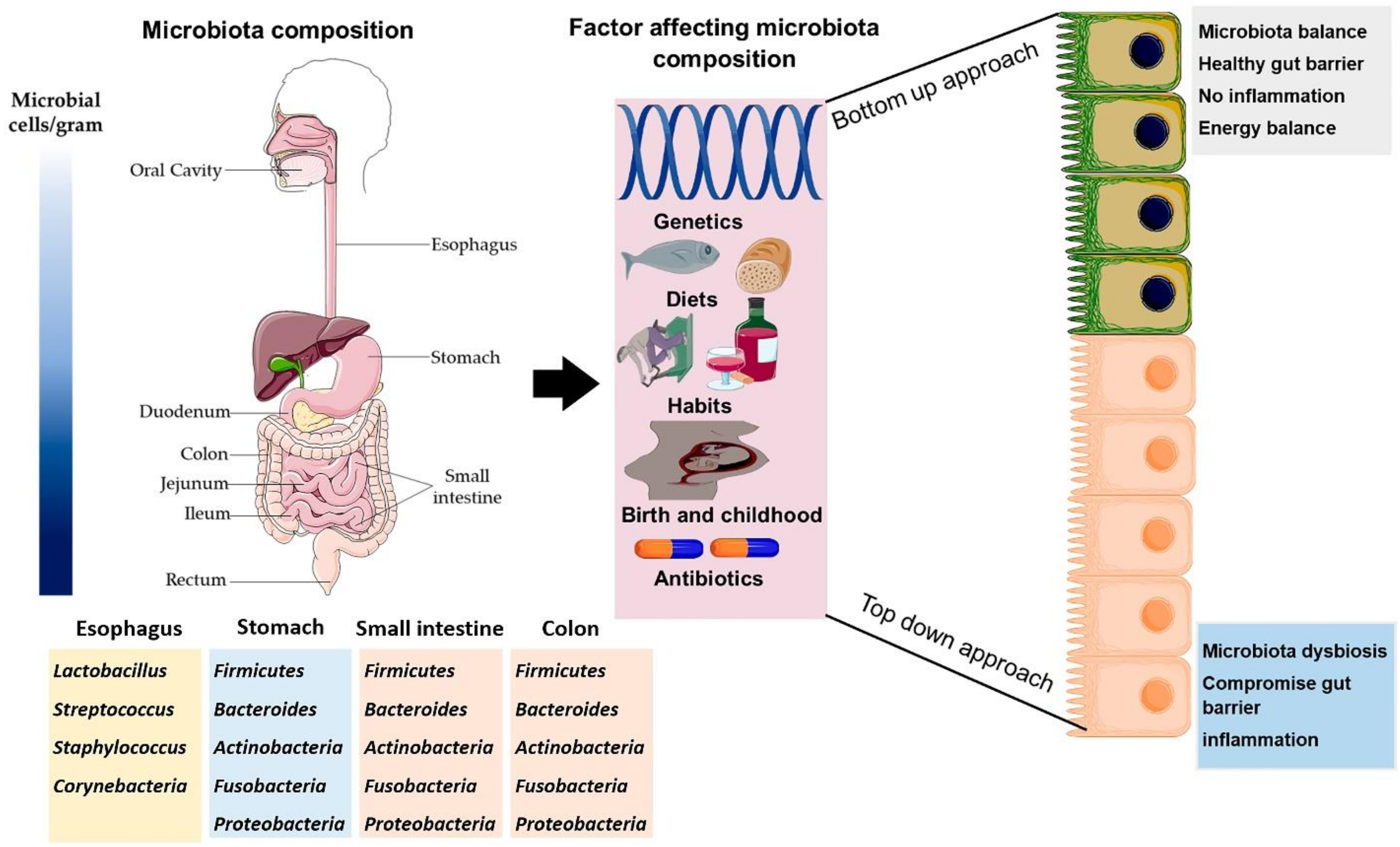
Antioxidants, Free Full-Text
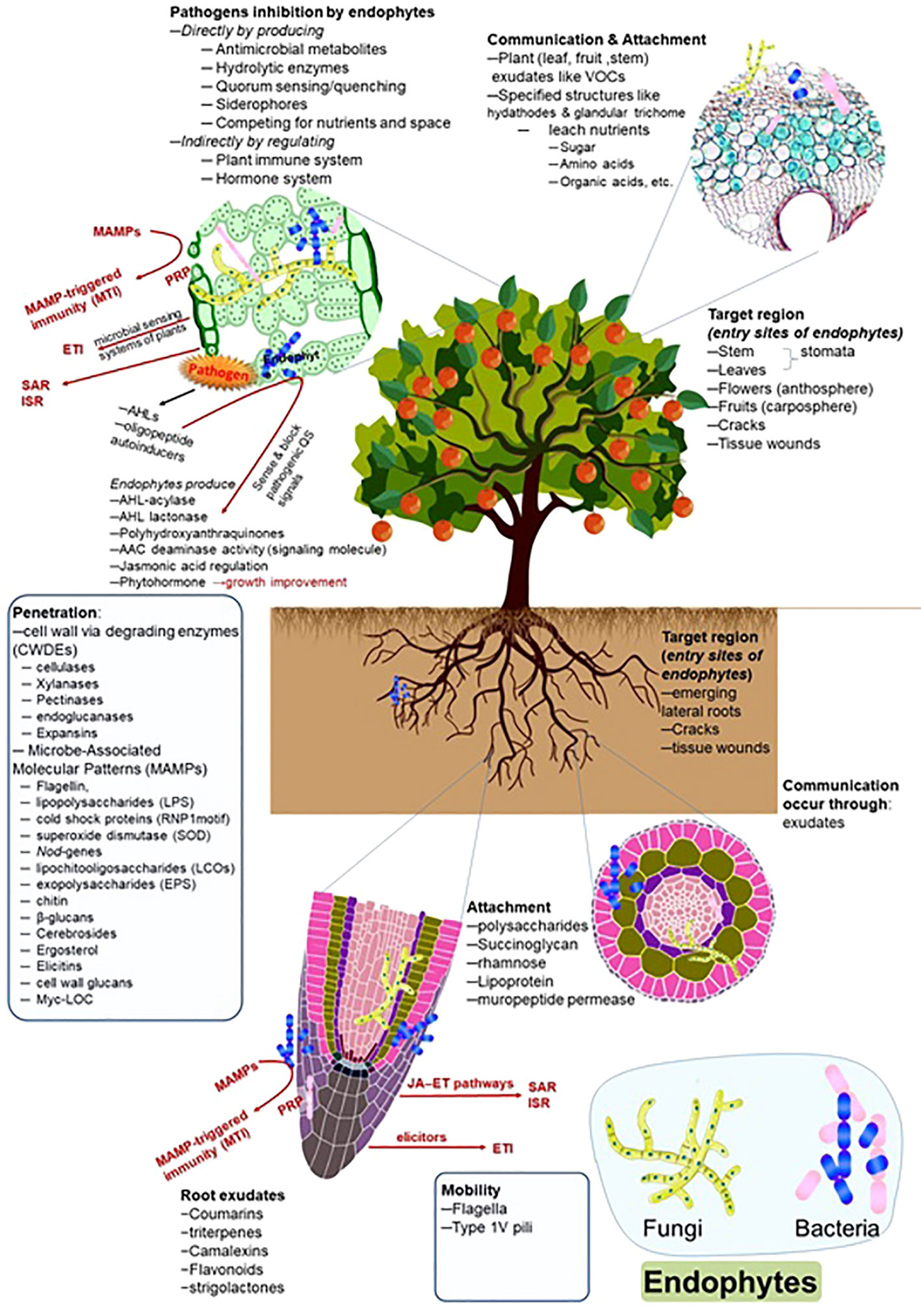
Frontiers Deciphering the role of endophytic microbiome in postharvest diseases management of fruits: Opportunity areas in commercial up-scale production
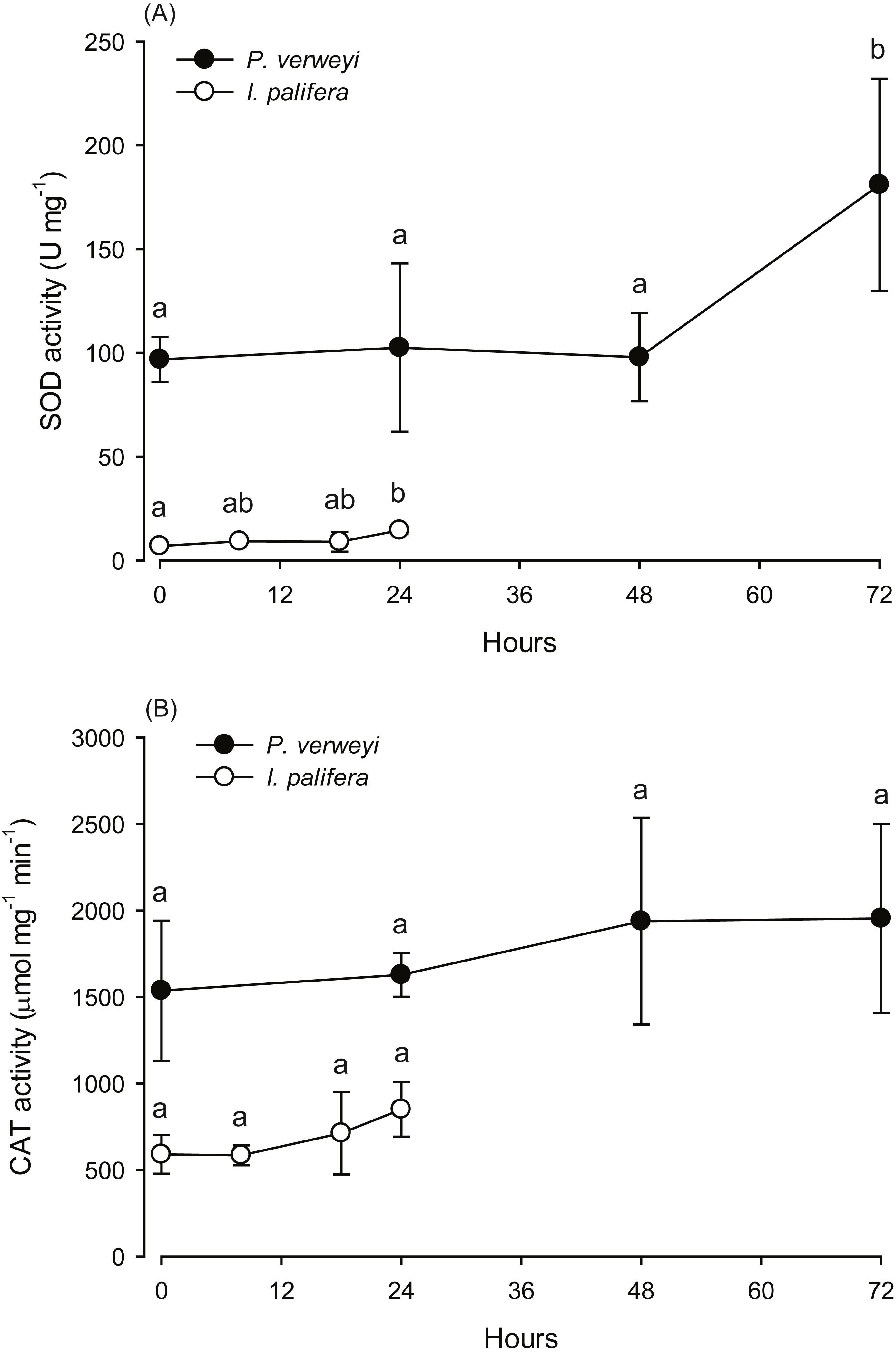
Extra high superoxide dismutase in host tissue is associated with improving bleaching resistance in “thermal adapted” and Durusdinium trenchii-associating coral [PeerJ]

Extracellular Superoxide Dismutase - an overview
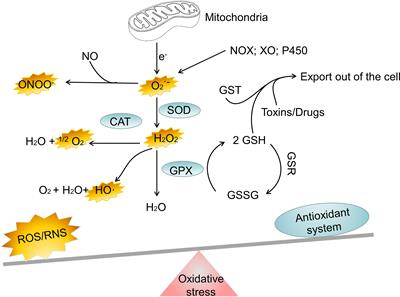
Frontiers Signaling pathways of oxidative stress response: the potential therapeutic targets in gastric cancer
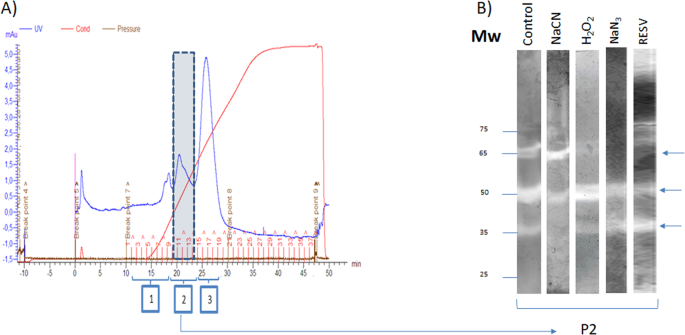
Identification and Molecular Characterization of Superoxide Dismutases Isolated From A Scuticociliate Parasite: Physiological Role in Oxidative Stress
Recomendado para você
-
Vagas Emdia - 📈Vagas de Control Desk Pleno, pra quem já manda16 junho 2024
-
 Empresa abre vaga de emprego em Salgueiro, PE; confira! - Blog do16 junho 2024
Empresa abre vaga de emprego em Salgueiro, PE; confira! - Blog do16 junho 2024 -
 Successful Premiere at Control Trade Show for QATM16 junho 2024
Successful Premiere at Control Trade Show for QATM16 junho 2024 -
 Hospital Tacchini abre 62 vagas de trabalho para equipe de16 junho 2024
Hospital Tacchini abre 62 vagas de trabalho para equipe de16 junho 2024 -
 In Debate With DeSantis, Newsom Can't Admit California's Policy16 junho 2024
In Debate With DeSantis, Newsom Can't Admit California's Policy16 junho 2024 -
 LG CEO and Key Executives Outline Directions To Diversify Business16 junho 2024
LG CEO and Key Executives Outline Directions To Diversify Business16 junho 2024 -
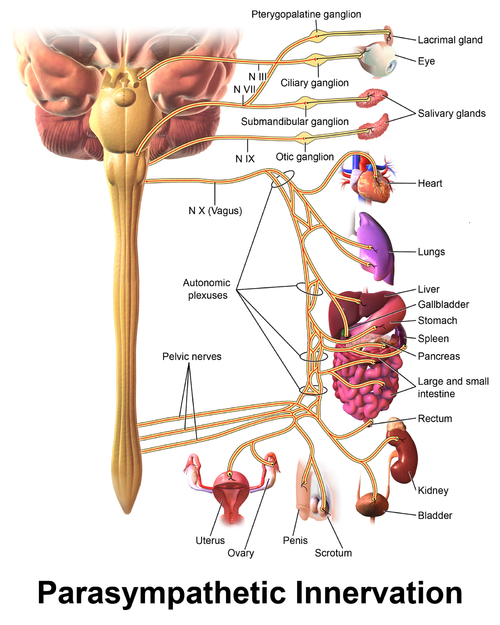 Vagus Nerve - Physiopedia16 junho 2024
Vagus Nerve - Physiopedia16 junho 2024 -
 Edição de hoje16 junho 2024
Edição de hoje16 junho 2024 -
 Ford oferece curso de tecnologia para pessoas de baixa renda16 junho 2024
Ford oferece curso de tecnologia para pessoas de baixa renda16 junho 2024 -
 carga de trabalhos :: emprego na área da comunicação16 junho 2024
carga de trabalhos :: emprego na área da comunicação16 junho 2024
você pode gostar
-
 In My Shadow Jumpsuit - White, Fashion Nova, Jumpsuits16 junho 2024
In My Shadow Jumpsuit - White, Fashion Nova, Jumpsuits16 junho 2024 -
 Mahjongg Minute16 junho 2024
Mahjongg Minute16 junho 2024 -
 Manchester United x Wolverhampton: onde assistir, escalações, arbitragem16 junho 2024
Manchester United x Wolverhampton: onde assistir, escalações, arbitragem16 junho 2024 -
 IHOP, Salina - 535 W Diamond Dr - Menu, Preços & Comentários de16 junho 2024
IHOP, Salina - 535 W Diamond Dr - Menu, Preços & Comentários de16 junho 2024 -
 Billiard room - Wikipedia16 junho 2024
Billiard room - Wikipedia16 junho 2024 -
 Brinquedo Jogo De Boliche Colorido No Ovo Lider16 junho 2024
Brinquedo Jogo De Boliche Colorido No Ovo Lider16 junho 2024 -
 This is the best time to visit Universal Studios Orlando Universal studios orlando, Universal studios, Universal vacation16 junho 2024
This is the best time to visit Universal Studios Orlando Universal studios orlando, Universal studios, Universal vacation16 junho 2024 -
 Resident Evil 4 Remake PC Trainer Infinite Health Items Ammo Unlimited Pesetas No Recoil Cheat FLiNG16 junho 2024
Resident Evil 4 Remake PC Trainer Infinite Health Items Ammo Unlimited Pesetas No Recoil Cheat FLiNG16 junho 2024 -
 Withered Freddy in 2023 Fnaf movie, Fnaf, Five night16 junho 2024
Withered Freddy in 2023 Fnaf movie, Fnaf, Five night16 junho 2024 -
 Piratas em ação: relatório lista as séries e filmes mais pirateados em 202116 junho 2024
Piratas em ação: relatório lista as séries e filmes mais pirateados em 202116 junho 2024
